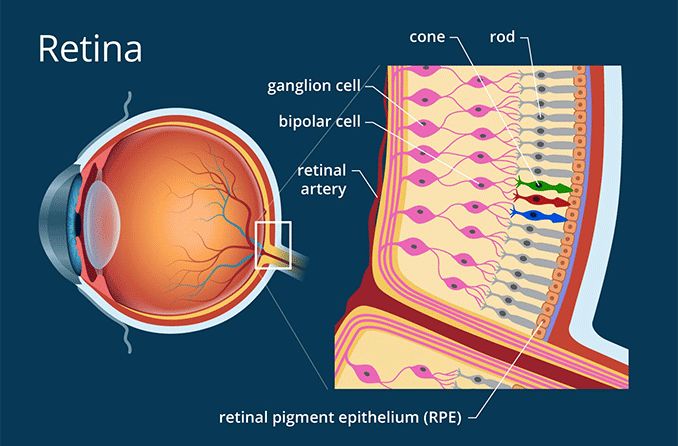
we specialize in providing exceptional care for your retina. The retina is a crucial part of the eye responsible for processing visual information and sending nerve impulses to the brain for visual perception.
The retina consists of several layers of neurons and is supported by an outer layer of pigmented epithelial cells. It plays a vital role in creating a focused two-dimensional image of the visual world, which is then transmitted to the brain through the optic nerve.
Sri Kota saidiah Nethralayam is committed to offering the highest quality retina care services to ensure the health and well-being of your vision.
The retina is a complex structure with ten distinct layers, each serving a specific function. It includes layers such as the inner limiting membrane, nerve fiber layer, ganglion cell layer, inner plexiform layer, inner nuclear layer, outer plexiform layer, outer nuclear layer, external limiting membrane, inner segment/outer segment layer, and the retinal pigment epithelium.
Inverted in vertebrates, the retina's light-sensing cells, rods, and cones, play a crucial role in vision. Rods function in dim light, providing monochromatic vision, while cones function in well-lit conditions, enabling color perception and high-acuity vision.
Regular retina care is essential for maintaining optimal vision. Conditions affecting the retina, such as retinal diseases, can manifest with symptoms like floaters, flashes, and loss of peripheral vision. Early detection and timely intervention can prevent vision loss and preserve eye health.

Micro Incision Cataract Surgery (MICS) is an advanced subtype of cataract surgery designed to treat cloudy formations in the eyes. This cutting-edge treatment utilizes sophisticated surgical tools, enabling surgeons to achieve improved results. The key feature of MICS is the use of minimal incisions, typically around 1.8 mm, making it a preferred option for minimal invasive cataract surgery.
MICS employs the Phacoemulsification technique, where the cataract is broken down using an ultrasound probe and then removed through suction methods.
After MICS, a unifocal lens implant is commonly used to restore vision. This enables patients to resume routine activities, although the use of glasses may still be necessary for tasks like reading or sewing. Wearing glasses for distance viewing can also be beneficial.
Various types of lenses are available in the market, including:
In the case of a unifocal lens implant, patients often rely on glasses, but the overall satisfaction rate with vision restoration is high.
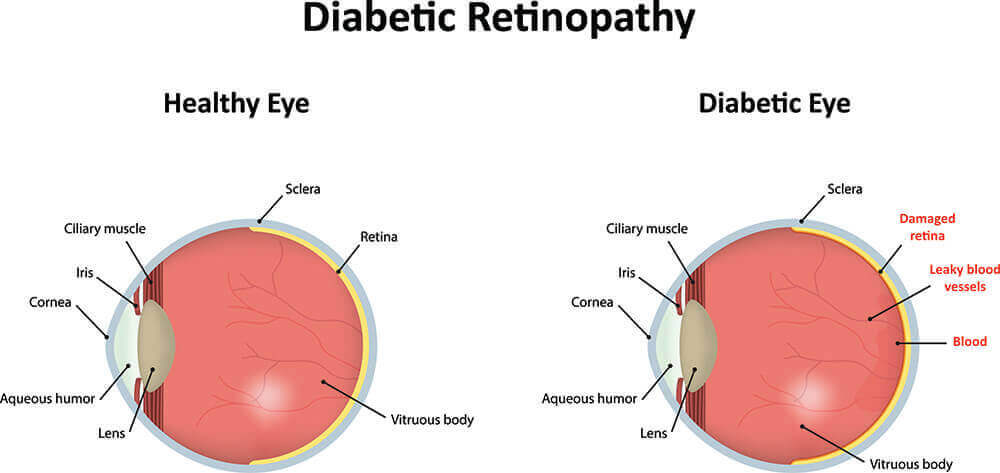
we understand the impact of diabetes on eye health. Diabetes can affect your eyes when blood glucose levels are consistently high, leading to potential complications that may threaten your vision.
While short-term changes in blood glucose may result in temporary blurry vision, long-term high glucose levels can cause damage to the tiny blood vessels in the back of your eyes.
This damage can start during prediabetes and progress to serious diabetic eye diseases. The following are some of the eye diseases associated with diabetes:
The retina, located at the back of each eye, is crucial for processing visual information. Diabetic retinopathy is a condition where damaged blood vessels in the retina can lead to vision problems.
In the early stages, blood vessels may weaken, bulge, or leak into the retina, known as nonproliferative diabetic retinopathy. If the condition worsens, new blood vessels may grow on the retina's surface, leading to proliferative diabetic retinopathy and serious vision issues.
Maintaining optimal blood glucose levels is essential for preventing diabetes-related eye complications. Regular eye examinations, early detection, and timely intervention are crucial in preserving your vision and overall eye health.
Our commitment to your eye health extends to diabetes-related concerns. We offer support services, ensuring that you can access professional advice and support for managing diabetes and its impact on your eyes. Your vision is our priority, and we are here for you every step of the way.
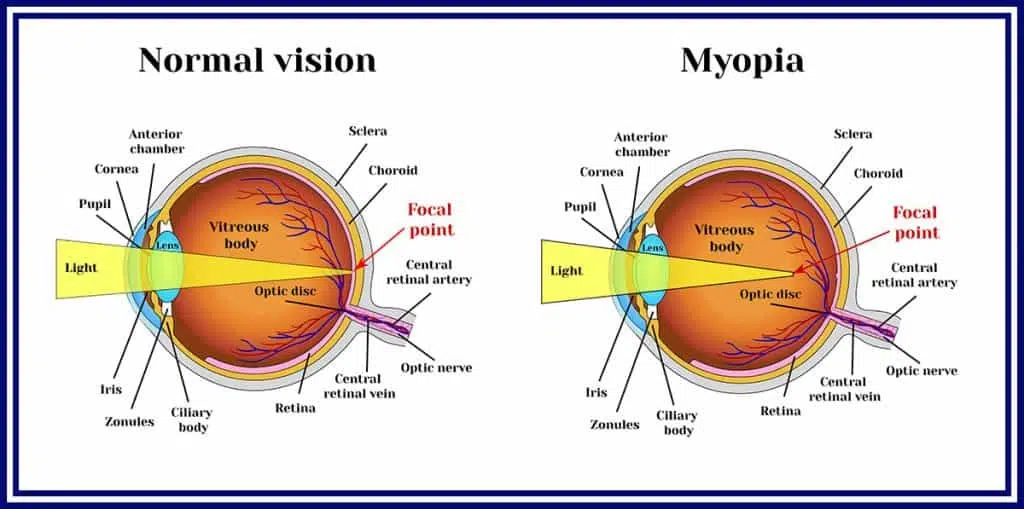
we specialize in addressing myopia, also known as near-sightedness or short-sightedness. Myopia is an eye condition where light from distant objects focuses in front of the retina, resulting in blurred vision for distant objects while close objects appear normal.
Common symptoms of myopia include headaches, eye strain, and difficulty seeing clearly at a distance. Severe myopia is associated with an increased risk of conditions such as macular degeneration, retinal detachment, cataracts, and glaucoma.
Myopia is often caused by the eyeball growing too long or, less commonly, by the lens being too strong. Both genetic and environmental factors contribute to the development of myopia, with risk factors including prolonged close-up work, spending more time indoors, urbanization, and a family history of the condition.
Diagnosis of myopia is conducted through eye examinations using cycloplegics. Myopia can be corrected using eyeglasses, contact lenses, or refractive surgery. Eyeglasses are a safe and simple method of correction, while contact lenses offer a wider corrected field of vision. Refractive surgeries like LASIK and PRK permanently change the cornea's shape.
Tentative evidence suggests that spending more time outdoors, especially during childhood, may decrease the risk of myopia. Regular eye examinations and early intervention are essential for managing myopia and preventing complications.
Myopia is the most common eye problem globally, affecting approximately 1.5 billion people (22% of the world population). Rates vary across regions, with increasing prevalence since the 1950s. Uncorrected myopia is a leading cause of vision impairment worldwide, alongside other eye conditions.
The term "myopia" has its origin in Koine Greek, meaning 'short-sight.' It is derived from words meaning 'to shut the eyes' and 'eye, look, sight.' The opposite of myopia is hyperopia or far-sightedness.
Genetic factors play a significant role in myopia, with studies identifying multiple loci associated with the condition. The contribution of genetic factors to myopia is estimated to be 60–90% of variance in refraction.
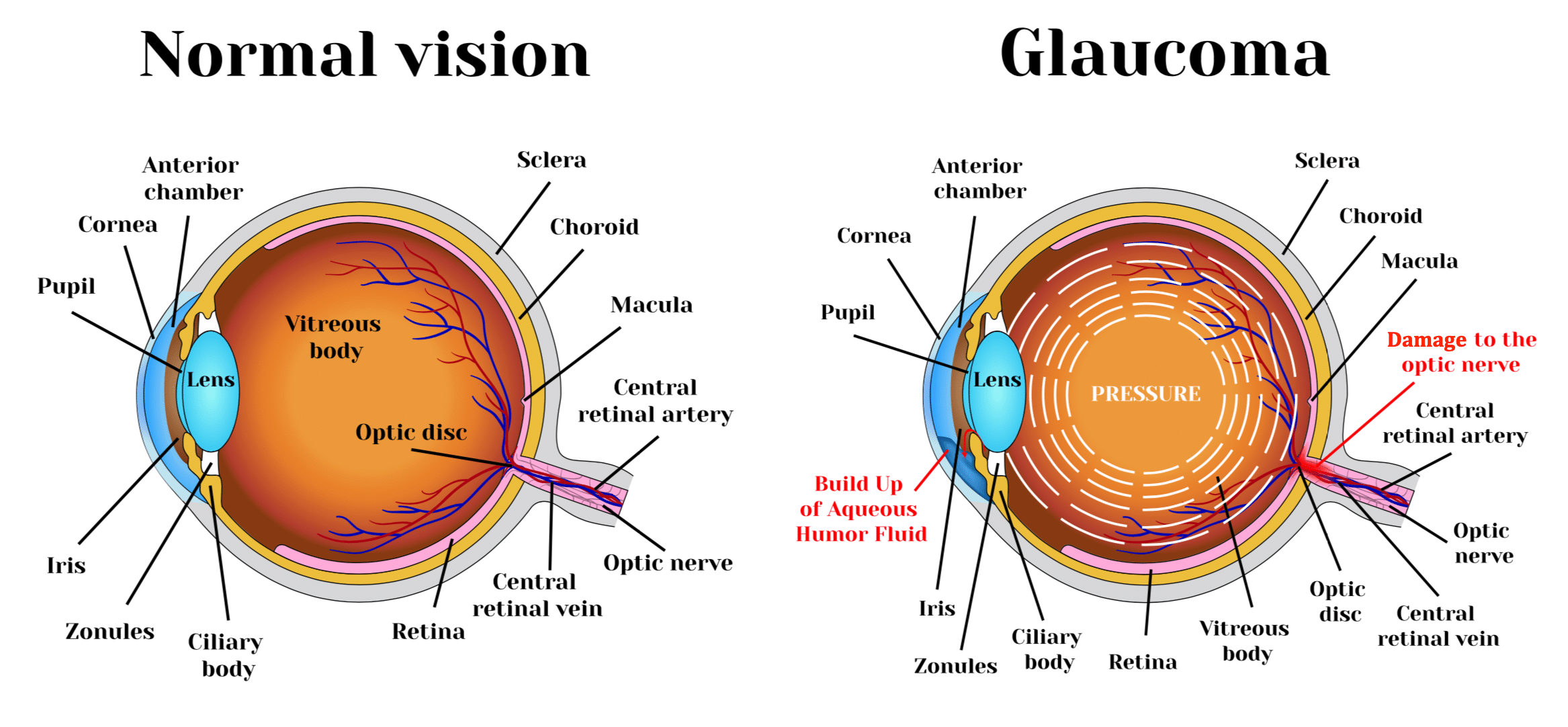
we are dedicated to addressing glaucoma, a group of eye conditions that can damage the optic nerve. The optic nerve is crucial for sending visual information from your eye to your brain, playing a vital role in maintaining good vision.
Glaucoma is often related to high pressure in the eye, but it can occur even with normal eye pressure. It can affect individuals at any age but is more common in older adults and is a leading cause of blindness for people over the age of 60.
Many forms of glaucoma have no warning signs, and the effects can be gradual. Regular eye exams, including measurements of eye pressure, are essential for early detection. If recognized early, vision loss can be slowed or prevented with proper treatment and monitoring.
The symptoms of glaucoma depend on the type and stage of the condition:
Regular eye exams and awareness of symptoms are crucial for early detection and effective management of glaucoma. If you suspect any symptoms or have concerns about your eye health, we at SRI KOTA SAIDIAH NETHRALAYAM are here to provide comprehensive care.
our focus extends to the unique visual needs of children through our specialized pediatric ophthalmology services. Pediatric ophthalmologists are experts in the development of the visual system and the various eye diseases that can impact children's visual health.
Dr Alla Stimitha is qualified to perform complex eye surgeries and manage various ocular diseases affecting children. Children with vision problems, eye misalignments, or other eye-related issues are often referred to a pediatric ophthalmologist for comprehensive evaluation and management.
Collaborating with orthoptists, Dr Alla Stimitha, pediatric ophthalmologist ensures comprehensive care for conditions like strabismus. We understand the importance of early detection and tailored interventions to support optimal visual development in children.
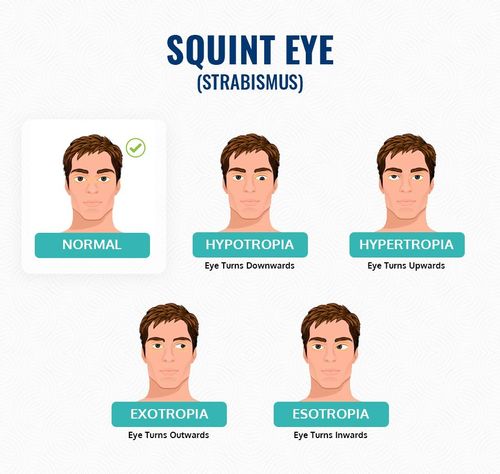
we specialize in the diagnosis and treatment of squint, also known as strabismus. Squint is a medical condition where the eyes do not align properly, leading to a lack of coordination in their movement.
This condition occurs due to poor control of eye muscles, an imbalance in eye muscles, faulty nerve signals to the eye muscles, or focusing issues, especially in cases of long-sightedness. The misalignment can cause the eyeballs to converge or diverge, affecting proper eye function.
Squint can manifest at any age, and it's crucial to seek consultation if a child develops the condition after 6-7 weeks of birth. Early detection and timely treatment are essential for optimal results.
We at SRI KOTA SAIDAIAH NETRALAYAM hospital is dedicated to providing comprehensive care for squint, addressing the underlying causes, and implementing effective treatment plans to correct eye alignment and improve overall eye function.
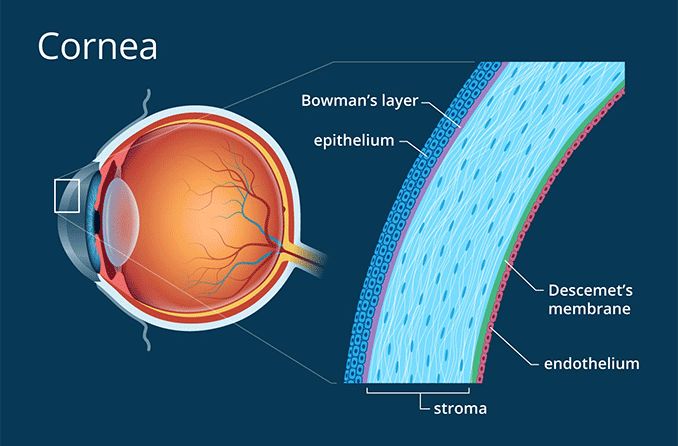
The cornea is a vital component of the eye responsible for clear vision. Situated at the front of the eye, it performs the crucial function of refracting light and focusing it onto the retina, allowing us to see the world around us.
The cornea is a complex structure composed of five layers:
The lack of blood vessels in the cornea contributes to its transparency. However, it also means that nutrients are supplied through tears and the aqueous humor in the anterior chamber. The cornea has a remarkable ability to repair itself from minor abrasions, but deeper injuries may lead to scarring and visual impairment.
Protecting the cornea is crucial for maintaining good eye health. Avoiding eye injuries, using protective eyewear, and practicing good hygiene can help prevent issues that may affect the cornea's clarity and function.
If you experience any discomfort, changes in vision, or suspect corneal issues, it's essential to seek professional eye care. Our team is here to provide comprehensive cornea care, ensuring the health and functionality of this vital eye component.